Financial institutions continue to face increasing pressure to adopt new technologies and pursue a customer-centric focus while balancing shifting regulatory requirements and an evolving marketplace. Some markets have cycled through digital disruption, but others are looking to prepare for future challenges and opportunities without disrupting business in 2019.
In today’s connected world the name of the game is instant gratification. Let’s say you’re interested in procuring a solar panel to power your shed this spring. You can conduct research, make your purchase, and have the package delivered to your doorstep in two days or less, completing all steps without leaving your house in under 30 minutes. Do you need someone to install the panel for you? Simply add on the installation service before checking out and your shed could be powered in as little as three days. How does this new social norm and behavior affect financial institutions and their customer experience? In more ways than one.
Fast, automated and personalized experiences, like Amazon Day, have become mainstream. In order to remain competitive, the financial services industry is working to meet these new demands alongside changing technology, new customer segments, an evolving marketplace and a shifting regulatory environment.
Customer Expectations
A changing customer profile that includes aging populations, Millennials, and Generation Z–the newest generation to hit the workforce– is demanding financial services and products that fit their lifestyle and their beliefs. An emphasis on convenience, social responsibility, and transparency can provide financial institutions an upper hand when vying for their attention and their money. Consumers are demanding simple and fast solutions that make them feel good throughout their journey.
“Financial institutions need to shift from physical interactions to digital engagement. For banks and credit unions that digitize client journeys, there can be a significant benefit in revenues, cost reductions and customer satisfaction.”

Convenience
If smartphones allow us to order our groceries, buy new shoes, and pay our bills through mobile apps, it’s safe to say we’re going to start forming generalized expectations about user experiences across industries. These expectations extend to connectivity, where the prevalence of financial management apps requires our full transparency and consent as customers in order to share data between primary banks and apps. Mobile applications that eliminate friction during the customer journey are a must for this audience’s adoption and continued use of financial services and products.
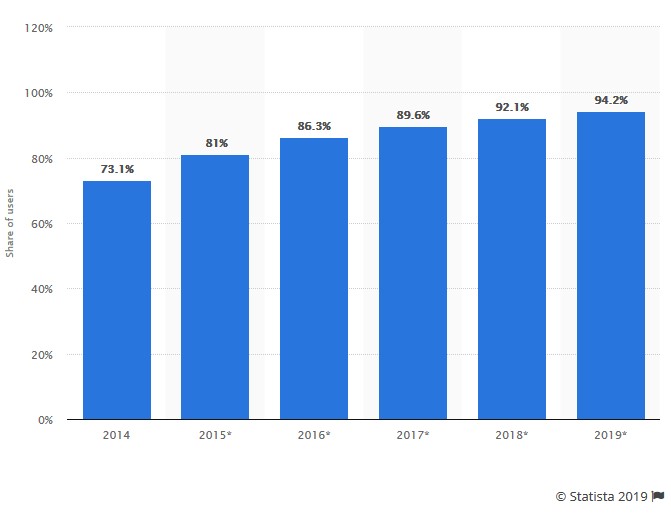
Share of Millennials using mobile phone banking in the United States from 2014 to 2019
If there are similar services being offered that are simpler to use and less time consuming, you can bet customers will find their way to them. One of these services is U.S. financial technology (fintech) startup Stripe, a service to help online sellers provide flexible billing and payments. Stripe is the most highly valued private fintech company in America (valued at $22.5 B) with clients like Amazon, Warby Parker and the National Football League.
Seizing Opportunity
Financial institutions are considering other tech trends to facilitate the fluid experience customers require. These trends include faster payments, speech recognition software, security biometrics, automated savings tools, and more control over personal data.
Strategic and technologically advanced financial institutions are leveraging application programming interfaces (APIs), Artificial Intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, data insights, and partnerships outside their expertise to meet customer expectations and distinguish themselves from competitors. Firms will find, if they haven’t already, that innovation on behalf of the customer is a win-win situation.
Benefits of Meeting Increased Customer Expectations:
- Enhanced customer experience
- Increased agility
- New revenue streams
- Enhanced operational efficiencies
- Access to additional customer data
- New products and services
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)

As younger and socially aware consumers begin relationships with banks and credit unions, financial institutions must create an experience beyond what’s offered at a traditional provider.
Over the past few years it seems Millennials have received the most attention from businesses, the media and popular culture. That being said, it is actually Generation Z (those born after the mid-1990s) that has entered the workforce and consumer marketplace and is expected to make up 40% of consumers globally by 2020, according to GeoMarketing. The newest generation to start contributing to the economy are considered early adopters and digital natives, who will seek simple technology, more options, and a greater need for acceptance and transparency within the organizations with which they are doing business. They are a cause-oriented generation who would like the companies they frequent to be activists for issues like the environment, climate change, and human rights. It’s clear the new generations want to work for and do business with socially responsible organizations.
There are real gains on hand for banks that have well-designed and successful CSR strategies. The Corporate Governance Institute lays out a few of these advantages for banks including:
- Positive publicity and/or increased brand recognition
- Encourages sustainable behavior by customers
- Provides real-world benefits for the society as a whole
- Elevates employee morale, motivation, and performance
Regulatory Compliance

Recent news in the U.S. and Sweden shows that the consequences of not meeting regulatory requirements has become increasingly burdensome. Regulatory missteps are very costly mistakes for financial institutions today. Understandably this has led to greater concern about risk and compliance management. Working to uphold regulatory compliance while satisfying evolving customer expectations have become critical marketplace demands for financial institutions.
Data Privacy
Failures in security and concerns about how companies are using customers’ personal data have led to an increased focus on data and customer privacy. The media has also heightened public awareness of data privacy and data protection with consistent reporting about the dangers and risks of social media.
Data privacy also brings with it risks to banks and financial services organizations. Key privacy concerns include: data security, privacy compliance reporting requirements, potential for large fines and penalties, and the need for effective data management. Financial institutions will also have to skillfully balance Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements with data privacy requirements across jurisdictions. Per the transition related to the Financial Account Standards Board update, firms will also be adopting the Current Expected Credit Loss (CECL) model, to measure credit losses for loans and debts securities.
The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires companies to protect consumer data, guarantee their customers certain rights related to their personal data and pay hefty fines if those rights are violated. In the United States, data breach notification laws have been implemented in all 50 states as of May 2018. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) goes into effect January 1, 2020, and was passed in a week, highlighting the need for lawmakers to take immediate action. All sectors of the finance industry must continue monitoring developments in consumer privacy protection laws at the state and federal level to maintain compliance.
Regulatory Compliance and Technology
Data, analytics, machine learning, and SaaS can assist with the customer experience and provide a competitive advantage for financial institutions, but may also expose them to unexpected risks. Data privacy and protection must be addressed to avoid regulatory hurdles when it comes to incorporating technology.
Technology Challenges:
- Standardizing data across jurisdictions or products
- Instilling the necessary culture change
- Ensuring the technology fulfills compliance requirements
- Finding technology that delivers as expected
- Having accurate and up-to-date data
- Cybersecurity concerns
- Hiring, training and retaining qualified staff
- Internal commercial and legal review
Success in 2019

To be successful in 2019, firms need to be able to handle continuous change and disciplined enough to meet regulatory requirements.
If you’re looking for due diligence expertise pertaining for financial institutions, Prescient can manage your financial, legal, regulatory, and reputational challenges so you can identify your risks and maximize your opportunities. Explore our due diligence services for your firm.
